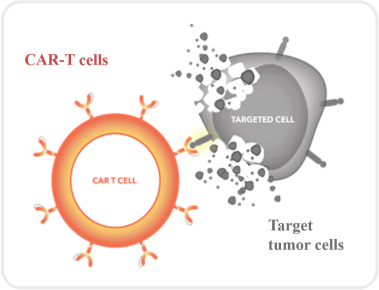
What are CAR-T cells?
CAR-T cells, or Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cells, are immunocytes engineered through genetic modification to actively track and destroy hematologic malignancies. By introducing the CAR gene, T-cells gain the ability to recognize cancer cells, enabling highly specific targeted attacks. This therapeutic approach has demonstrated success in lymphoma, leukemia, and multiple myeloma, offering new hope for patients.
- Consensus of Chinese Experts on the CAR-T Cell Therapy in Moltiple Myeloma (2022).
- Bourré L. How to Assess CAR-T Cell Therapy in Preclinical Evaluation. Crown Bioscience (2018).
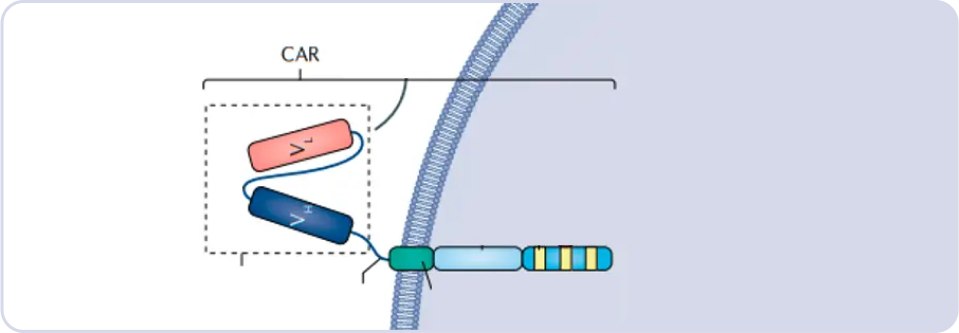
What is the CAR structure?
Larson RC, Maus MV. Recent advances and discoveries in the mechanisms and functions of CAR T cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021 Mar;21(3):145-161.
What are CAR-T cells?
CAR, or Chimeric Antigen Receptor, employs the single-chain variable fragment (scFv) of an antibody to identify tumor antigens. Based on the source of scFv, CAR-T cells can be categorized into murine-derived, camelid-derived (llama), and fully human-derived, each contributing distinct characteristics to enhance the specificity and efficacy of the CAR-T cell therapy.
There are significant distinctions between animal-sourced CAR-T cells, including murine and camelid origins, and fully human-sourced CAR-T cells in both manufacturing processes and clinical applications. Animal-sourced CAR-T cells, prone to provoke immune responses due to their non-human origin, may include murine and camelid-derived structures. Conversely, fully human-sourced CAR-T cells, derived entirely from human components, reduce the risk of immunogenicity. Clinical evidence suggests that fully human-sourced CAR-T cells exhibit superior performance in reducing adverse reactions and enhancing therapeutic efficacy. As a result, they are gaining increasing attention in the development of CAR-T cell therapies.
Rui Cui, Ping Li, Qing Li, et al. Salvage therapy with humanized BCMA CAR-T cells in two cases with refractory multiple myeloma that progressed after treatment with murine BCMA CAR-T cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Hematology, 2021, 42 (6): 502-507.
How are CAR-T cells prepared?
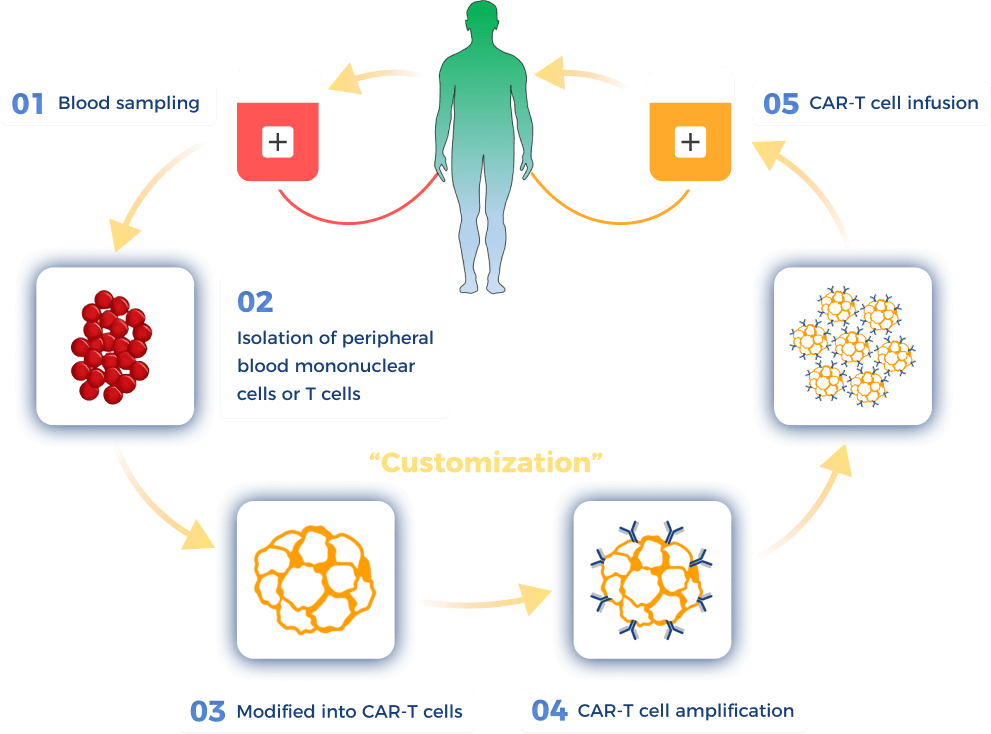
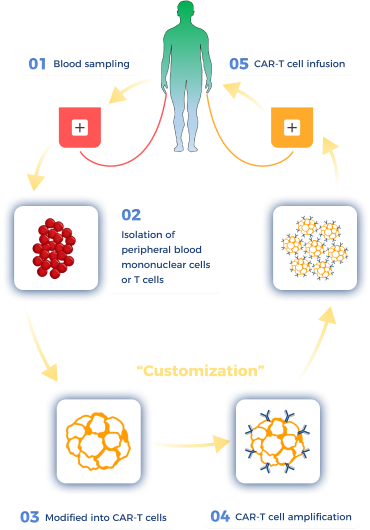
Watanabe N, Mo F, McKenna MK. Impact of Manufacturing Procedures on CAR T Cell Functionality. Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 13;13:876339.
What is the difference between CAR-T therapy and traditional tumor therapy?
Efficacy and Safety of CAR-T Therapy
While CAR-T cell therapy offers potent efficacy, it is accompanied by potential safety risks. Post-treatment reactions vary due to individual differences and may include cytotoxic reactions, cytokine release syndrome, and neurotoxicity. Nevertheless, studies indicate significant sustained remission and long-term efficacy for many hematologic malignancy patients undergoing CAR-T therapy. Physicians closely monitor patient responses post-treatment, implementing appropriate measures to maximize efficacy and minimize potential risks, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of CAR-T therapy.
What questions might I ask my CAR T treatment team?
- Am I a candidate for CAR T cell therapy?
- How is CAR T therapy expected to benefit my specific type of cancer?
- Will I need a caregiver or support person during the treatment?




